排序算法 高效交换算法(异或^) 概念
0^N = N ; N^N = 0
相同为0,不同为1,也可以叫做无进位相加,这么做的前提:需要交换的两个数指向的内存是两位位置
异或运算满足交换律和结合律
不用额外变量交换两个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 public static void swap (int [] arr, int i, int j) arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j]; arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j]; }
一种数出现奇数次 一个数组中有一个数出现奇数次,其他数都出现偶数次,怎么找到这一个数?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public static void printOddTimesNum1 (int [] arr) int eor = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { eor ^= arr[i]; } System.out.println(eor); }
两种数出现奇数次 一个数组中有两个数出现奇数次,其他数都出现了偶数次,怎么找到这两个数?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public static void printOddTimesNum2 (int [] arr) int eor = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { eor ^= arr[i]; } int rightOne = eor & (-eor); int onlyOne = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length;i++) { if ((arr[i] & rightOne) != 0 ) { onlyOne ^= arr[i]; } } System.out.println(onlyOne + " " + (eor ^ onlyOne)); }
冒泡排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public static void bubbleSort (int [] arr) if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } for (int e = arr.length - 1 ; e > 0 ; e--) { for (int i = 0 ; i < e; i++) { if (arr[i] > arr[i + 1 ]) { swap(arr, i, i + 1 ); } } } }
在一趟排序过程中如果一次都没有交换过,那说明后续的数都是有序的,不需要在进行后续的排序了,如果元素本来就是有序的,就只比较一次就结束了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public static void bubbleSort (int [] arr) if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } boolean flag = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]) { flag = true ; int temp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1 ]; arr[j + 1 ] = temp; } } if (!flag) { break ; } else { flag = false ; } } }
选择排序
0 ~ N-1 找到最小值,在哪,放到0位置上
1 ~ n-1 找到最小值,在哪,放到1 位置上
2 ~ n-1 找到最小值,在哪,放到2 位置上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public static void selectionSort (int [] arr) if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length - 1 ; i++) { int minIndex = i; for (int j = i + 1 ; j < arr.length; j++) { minIndex = arr[j] < arr[minIndex] ? j : minIndex; } swap(arr, i, minIndex); } }
插入排序
0~1单范围有序
0~2范围有序
0~3范围有序
0~N范围有序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static void insertionSort (int [] arr) if (arr == null || arr.length < 2 ) { return ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.length; i++) { for (int j = i - 1 ; j >= 0 && arr[j] > arr[j + 1 ]; j--) { swap(arr, j, j + 1 ); } } }
查找算法 二分查找 二分法的详解与扩展
在一个有序数组中,查找某个数是否存在
在一个有序数组中,找>=某个数最左侧的位置
局部最小值问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static boolean exist (int [] sortedArr, int num) if (sortedArr == null || sortedArr.length == 0 ) { return false ; } int L = 0 ; int R = sortedArr.length - 1 ; int mid = 0 ; while (L < R) { mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1 ); if (sortedArr[mid] == num) { return true ; } else if (sortedArr[mid] > num) { R = mid - 1 ; } else { L = mid + 1 ; } } return sortedArr[L] == num; }
数组范围上求最大值 递归解法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public static int process (int [] arr, int L, int R) if (L == R) { return arr[L]; } int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1 ); int leftMax = process(arr, L, mid); int rightMax = process(arr, mid + 1 , R); return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax); }
对数器的概念
有一个你想要测试的方法a
实现复杂度不好但是容易实现的方法b
实现一个随机样本产生器
把方法a和方法b跑相同的随机样本,看看得到的结果是否一样
如果有一个随机样本时的比对结果不一致,打印样本进行人工干预,改对方法a或者方法b
当样本数量很多时比对测试依然正确,可以确定方法a已经正确
数组 ab数组合并到a
题目:给出两个有序的整数数组A和B,请将数组B合并到数组A中,变成一个有序的数组。注意:可以假设A数组有足够的空间存放B数组的元素,A和B中初始的元素数目分别为m和n。
题解:最优解:从后往前处理,不需要开辟额外空间。从后往前,这样不需要进行冗余处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static void merge (int [] a, int m, int [] b, int n) int i = m - 1 ; int j = n - 1 ; int index = m + n - 1 ; while (i >= 0 && j >= 0 ) { if (a[i] > b[j] ){ a[index--] = a[i--]; } else { a[index--] = b[j--]; } } while (j >= 0 ) { a[index--] = b[j--]; } }
ab数组合并到c
题目: 合并两个有序整型数据(入参两个需要合并的数组,返回值合并好的新数组)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private static int [] margeArr(int [] a, int [] b) { int [] c = new int [a.length + b.length]; int i = 0 , j = 0 ; int index = 0 ; while (i < a.length && j < b.length) { if (a[i] < b[j]) { c[index++] = a[i++]; } else { c[index++] = b[j++]; } } int l; if (i < a.length) { for (l = i; l < a.length; l++) { c[index++] = a[l]; } } if (j < b.length) { for (l = j; l < b.length; l++) { c[index++] = b[l]; } } return c; }
查找两数之和等于目标数
题目:给定一个数组和一个目标数,从数组中找到两个数,是这两个数之和等于目标数。返回其在数组中的编号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) { return new int []{map.get(target - nums[i]), i}; } map.put(nums[i], i); } return null ; }
螺旋打印二维数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 public static void printEdge (int [][] m, int tR, int tC, int dR, int dC) if (tR == dR) { for (int i = tC; i <= dC; i++) { System.out.print(m[tR][i] + " " ); } } else if (tC == dC) { for (int i = tR; i <= dR; i++) { System.out.print(m[i][tC] + " " ); } } else { int curC = tC; int curR = tR; while (curC != dC) { System.out.print(m[tR][curC] + " " ); curC++; } while (curR != dR) { System.out.print(m[curR][dC] + " " ); curR++; } while (curC != tC) { System.out.print(m[dR][curC] + " " ); curC--; } while (curR != tR) { System.out.print(m[curR][tC] + " " ); curR--; } } } public static void spiralOrderPrint (int [][] matrix) int tR = 0 ; int tC = 0 ; int dR = matrix.length - 1 ; int dC = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ; while (tR <= dR && tC <= dC) { printEdge(matrix, tR++, tC++, dR--, dC--); } } public static void main (String[] args) int [][] matrix = { { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 }, { 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 }, { 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 }, { 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 } }; spiralOrderPrint(matrix); }
链表
对于笔试,不用太在乎空间复杂度,一切为了时间复杂度
对于面试,时间复杂度依然放在第一位,但是一定要找到空间最省的方法
链表反转 单向链表反转 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public static class Node public int value; public Node next; public Node (int data) value = data; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static Node reverseLinkedList (Node head) Node pre = null ; Node next = null ; while (head != null ) { next = head.next; head.next = pre; pre = head; head = next; } return pre; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private Node reverseLinkedList (Node head) if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } Node newHead = reverseLinkedList(head.next); head.next.next = head; head.next = null ; return newHead; }
双向链表反转 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static class DoubleNode public int value; public DoubleNode last; public DoubleNode next; public DoubleNode (int data) value = data; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList (DoubleNode head) DoubleNode pre = null ; DoubleNode next = null ; while (head != null ) { next = head.next; head.next = pre; head.last = next; pre = head; head = next; } return pre; }
查找链表中点 快慢指针应用
查找链表中点或中点上一个 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static Node midOrUpMidNode (Node head) if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null ) { return head; } Node slow = head.next; Node fast = head.next.next; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } return slow; }
查找链表中点或中点下一个 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static Node midOrDownMidNode (Node head) if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return head; } Node slow = head.next; Node fast = head.next; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } return slow; }
判断一个链表是否是回文结构 【题目】给定一个单向链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。【例子】1->2->1,返回true;1->2->2->1,返回true;15->6->15,返回true;1->2->3,返回false。如果链表长度为N,时间复杂度达到O(N),额外空间复杂度达到O(1)。
解题思路1: 1:遍历链表,把每个元素放到栈里面;2:从栈里面依次弹出元素和原来链表挨个元素比对。解题思路2: 1:通过快慢指针找到中点和结束点,只把右侧部分放到栈里面去;2:从栈里面依次弹出元素和原来链表挨个元素比对。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static boolean isPalindrome1 (Node head) Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); Node cur = head; while (cur != null ) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.next; } while (head != null ) { if (head.value != stack.pop().value) { return false ; } head = head.next; } return true ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public static boolean isPalindrome2 (Node head) if (head == null || head.next == null ) { return true ; } Node right = head.next; Node cur = head; while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null ) { right = right.next; cur = cur.next.next; } Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (right != null ) { stack.push(right); right = right.next; } while (!stack.isEmpty()) { if (head.value != stack.pop().value) { return false ; } head = head.next; } return true ; }
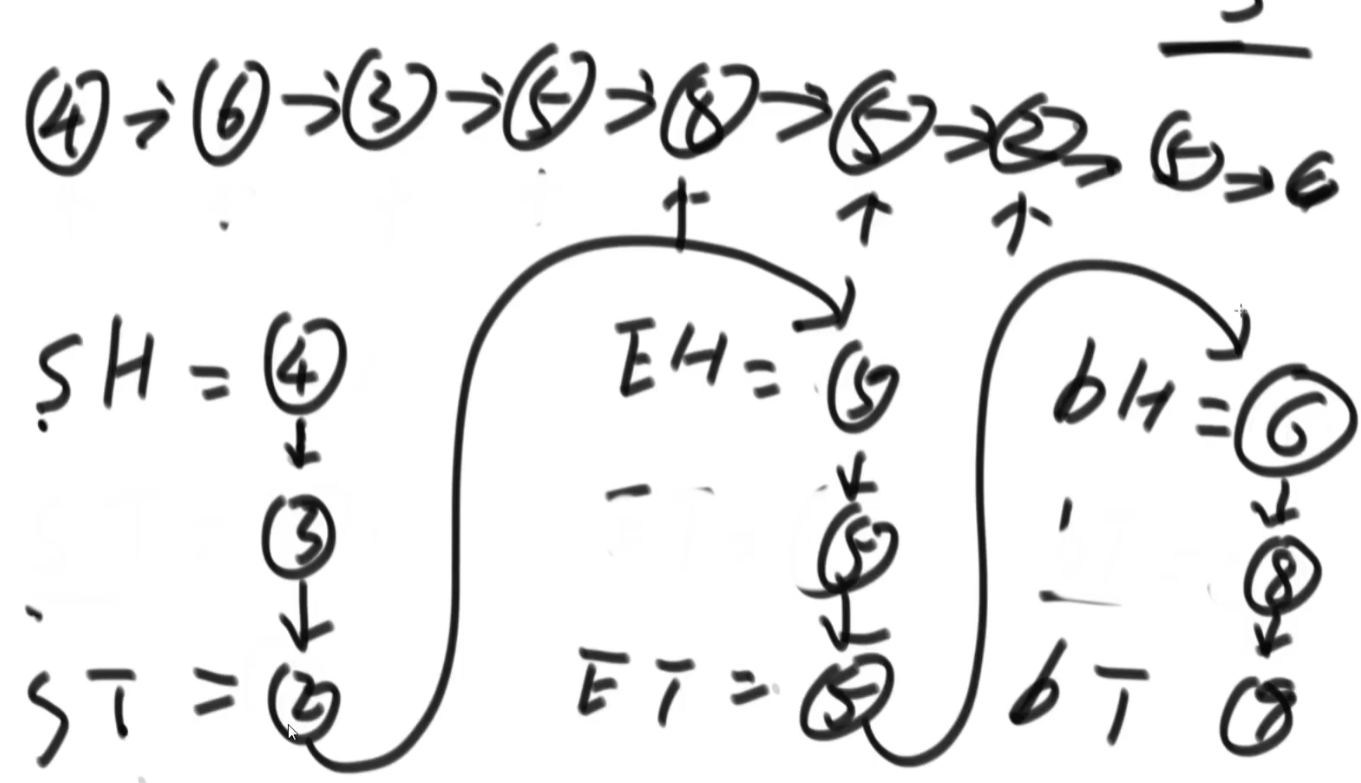
链表排序 单向链表分左中右 【题目】 将单向链表按照某值划分成左边小,中间相等,右边大的形式:给定一个单链表头节点head,节点的值类型是整型,再给定一个整数pivot。实现一个调整链表的函数,将链表调整为做部分都是值小于pivot的节点,中间部分都是值等于piovt的节点,有部分都是值大于piovt的节点。【进阶】在实现原问题功能的基础上增加要求:小于,等于,大于pivot节点之间顺序和之前一样,时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度O(1)。
解题思路1: 将链表放入数组,排序,再转成链表
解题思路2: 左中右分别准备两个指针(共6个变量),然后遍历原链表,排序之后分别插入相应位置(考虑边界问题)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public static Node listPartition1 (Node head, int pivot) if (head == null ) { return head; } Node cur = head; int i = 0 ; while (cur != null ) { i++; cur = cur.next; } Node[] nodeArr = new Node[i]; i = 0 ; cur = head; for (i = 0 ; i != nodeArr.length; i++) { nodeArr[i] = cur; cur = cur.next; } arrPartition(nodeArr, pivot); for (i = 1 ; i != nodeArr.length; i++) { nodeArr[i - 1 ].next = nodeArr[i]; } nodeArr[i - 1 ].next = null ; return nodeArr[0 ]; } public static void arrPartition (Node[] nodeArr, int pivot) int small = -1 ; int big = nodeArr.length; int index = 0 ; while (index != big) { if (nodeArr[index].value < pivot) { swap(nodeArr, ++small, index++); } else if (nodeArr[index].value == pivot) { index++; } else { swap(nodeArr, --big, index); } } } public static void swap (Node[] nodeArr, int a, int b) Node tmp = nodeArr[a]; nodeArr[a] = nodeArr[b]; nodeArr[b] = tmp; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 public static Node listPartition2 (Node head, int pivot) Node sH = null ; Node sT = null ; Node eH = null ; Node eT = null ; Node mH = null ; Node mT = null ; Node next = null ; while (head != null ) { next = head.next; head.next = null ; if (head.value < pivot) { if (sH == null ) { sH = head; sT = head; } else { sT.next = head; sT = head; } } else if (head.value == pivot) { if (eH == null ) { eH = head; eT = head; } else { eT.next = head; eT = head; } } else { if (mH == null ) { mH = head; mT = head; } else { mT.next = head; mT = head; } } head = next; } if (sT != null ) { sT.next = eH; eT = eT == null ? sT : eT; } if (eT != null ) { eT.next = mH; } return sH != null ? sH : (eH != null ? eH : mH); }
链表闭环及相交问题 单链表查找闭环位置 注:单链表闭环只能有一个环,如果产生环,必然会出现闭环
解法1:额外空间解决
申请一个set集合,从头节点遍历链表,每遍历一个元素就查询该节点是否在集合中,如果没有就把该节点放进去,如果有,该节点就是环位置
解法2:有限几个变量解决
快慢指针从单链表头节点开始走,直至两个节点相遇,说明有环,最后指向null,说明无环
相遇之后快指针回到头节点,之后一次走一步,慢指针停在原地,再次相遇的位置即是环节点位置(记住结论,不要问为什么)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static class Node public int value; public Node next; public Node (int data) this .value = data; } } public static Node getLoopNode (Node head) if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null ) { return null ; } Node slow = head.next; Node fast = head.next.next; while (slow != fast) { if (fast.next == null || fast.next.next == null ) { return null ; } fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } fast = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; }
两个无环链表交点位置 注:
如果两个单向链表相交,相交后面的部分必然是共有的,那么两个链表最后的那个节点必然是同一个节点
长链表先走两个链表差值的步数,然后短链表在开始走,他俩一定会在第一个相交的位置相遇
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public static Node noLoop (Node head1, Node head2) if (head1 == null || head2 == null ) { return null ; } Node cur1 = head1; Node cur2 = head2; int n = 0 ; while (cur1.next != null ) { n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2.next != null ) { n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } if (cur1 != cur2) { return null ; } cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0 ) { n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur1 != cur2) { cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } return cur1; }
两条有环链表查找交点 分为两种情况:入环节点可能是同一个节点,也可能不是同一个节点,如图
情况1:入环节点可能是同一个节点,就是求单链表的第一个环节点问题,只不过从相交位置开始走
情况2:如果链表1在转回到自己的过程中没有遇到链表2,就说明是各自成环的,相交节点返回空就醒来,如果遇到,就是情况2,返回两个节点,都对,都属于第一个相交的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 public static Node bothLoop (Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) Node cur1 = null ; Node cur2 = null ; if (loop1 == loop2) { cur1 = head1; cur2 = head2; int n = 0 ; while (cur1 != loop1) { n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2 != loop2) { n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0 ) { n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur1 != cur2) { cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } return cur1; } else { cur1 = loop1.next; while (cur1 != loop1) { if (cur1 == loop2) { return loop1; } cur1 = cur1.next; } return null ; } }
查找两个链表相交节点 注:难点为考虑是否有环,有环链表相交以及无环链表相交问题,没有用到额外数据结构,只用到有限几个变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static Node getIntersectNode (Node head1, Node head2) if (head1 == null || head2 == null ) { return null ; } Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1); Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2); if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null ) { return noLoop(head1, head2); } if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null ) { return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2); } return null ; }
二叉树 数据结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public static class Node public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node (int v) value = v; } }
二叉树遍历
先序遍历:头->左->右
中序遍历:左->头->右
后序遍历:左->右->头
递归遍历二叉树 遍历说明
递归通过打印时机不同,实现先,中,后序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static void f (Node head) if (head == null ) { return ; } f(head.left); f(head.right); }
非递归遍历二叉树
准备一个栈,根节点入栈弹出,打印,然后先压右,再压左
弹出打印,先压右再压左,周而复始
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static void pre (Node head) System.out.print("pre-order: " ); if (head != null ) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.add(head); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " " ); if (head.right != null ) { stack.push(head.right); } if (head.left != null ) { stack.push(head.left); } } } System.out.println(); }
在先序遍历的基础之上,增加一个收集栈,弹出来就放到收集栈中(不打印),然后先压左,再压右
把收集栈中的元素依次出栈,打印
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static void pos1 (Node head) System.out.print("pos-order: " ); if (head != null ) { Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); s1.push(head); while (!s1.isEmpty()) { head = s1.pop(); s2.push(head); if (head.left != null ) { s1.push(head.left); } if (head.right != null ) { s1.push(head.right); } } while (!s2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " " ); } } System.out.println(); }
整棵树左边界进栈,依次弹出的过程中,打印,对弹出节点的右树周而复始
为什么? 因为整个树都会被他的左边界分解掉,我们把头和左边界压栈,然后再右,出栈的时候就是左,头,右
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public static void in (Node cur) System.out.print("in-order: " ); if (cur != null ) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null ) { if (cur != null ) { stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; } else { cur = stack.pop(); System.out.print(cur.value + " " ); cur = cur.right; } } } System.out.println(); }
宽度遍历 宽度遍历就是横着遍历,也是层次遍历
用队列,头节点放队列,每一次弹出就打印,然后先放左再放右,每一个元素出队列都是先放左再放右
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static void width (Node head) if (head == null ) { return ; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(head); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = queue.poll(); System.out.println(cur.value); if (cur.left != null ) { queue.add(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ) { queue.add(cur.right); } } }
求二叉树的最大宽度(难) 分析:宽度性遍历的时候要知道每一层的节点个数
解:遍历每个节点的时候,知道他在第几层
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public static int maxWidthUseMap (Node head) if (head == null ) { return 0 ; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(head); HashMap<Node, Integer> levelMap = new HashMap<>(); levelMap.put(head, 1 ); int curLevel = 1 ; int curLevelNodes = 0 ; int max = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = queue.poll(); int curNodeLevel = levelMap.get(cur); if (cur.left != null ) { levelMap.put(cur.left, curNodeLevel + 1 ); queue.add(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ) { levelMap.put(cur.right, curNodeLevel + 1 ); queue.add(cur.right); } if (curNodeLevel == curLevel) { curLevelNodes++; } else { max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes); curLevel++; curLevelNodes = 1 ; } } max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes); return max; } public static int maxWidthNoMap (Node head) if (head == null ) { return 0 ; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.add(head); Node curEnd = head; Node nextEnd = null ; int max = 0 ; int curLevelNodes = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node cur = queue.poll(); if (cur.left != null ) { queue.add(cur.left); nextEnd = cur.left; } if (cur.right != null ) { queue.add(cur.right); nextEnd = cur.right; } curLevelNodes++; if (cur == curEnd) { max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes); curLevelNodes = 0 ; curEnd = nextEnd; } } return max; }
折纸问题
结果可看做头节点是凹,所有的左子树头节点都是凹,所有右子树头肩点都是凸的二叉树
中序遍历即可打印出从上到下的所有结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static void main (String[] args) int N = 4 ; process(1 , N, true ); } public static void process (int i, int N, boolean down) if (i > N) { return ; } process(i + 1 , N, true ); System.out.print(down ? "凹 " : "凸 " ); process(i + 1 , N, false ); }
搜索二叉树(递归套路)
题目: 如何判断一颗二叉树是搜索二叉树?搜索二叉树的特点: 任何一个节点,左子树的节点一定比它小,右子树的节点一定比它大解题: 中序遍历一定是升序,如果某个位置有降序,一定不是搜索二叉树递归套路题解 :向我左树要信息,右树要信息,左树必须是搜索二叉树且左树最大值小于我,右树是搜索二叉树并且最小值大于我;左树信息:1.是否是搜索二叉树,2.最大值,3.最小值;右树也是注意: 递归套路,可以解决一切树形DP 问题,无非是可能性的罗列有难度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static class Node public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node (int data) this .value = data; } } public static boolean isBST1 (Node head) if (head == null ) { return true ; } ArrayList<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>(); in(head, arr); for (int i = 1 ; i < arr.size(); i++) { if (arr.get(i).value <= arr.get(i - 1 ).value) { return false ; } } return true ; } public static void in (Node head, ArrayList<Node> arr) if (head == null ) { return ; } in(head.left, arr); arr.add(head); in(head.right, arr); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static int preValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public static boolean checkBST (Node head) if (head == null ) { return true ; } boolean checkLeft = checkBST(head.left); if (!checkLeft) { return false ; } if (head.value <= preValue) { return false ; } else { preValue = head.value; } return checkBST(head.right); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public static class Info public boolean isBST; public int max; public int min; public Info (boolean i, int ma, int mi) isBST = i; max = ma; min = mi; } } public static Info process (Node x) if (x == null ) { return null ; } Info leftInfo = process(x.left); Info rightInfo = process(x.right); int min = x.value; int max = x.value; if (leftInfo != null ) { min = Math.min(min, leftInfo.min); max = Math.max(max, leftInfo.max); } if (rightInfo != null ) { min = Math.min(min, rightInfo.min); max = Math.max(max, rightInfo.max); } boolean isBST = true ; if (leftInfo != null && !leftInfo.isBST) { isBST = false ; } if (rightInfo != null && !rightInfo.isBST) { isBST = false ; } if (leftInfo != null && leftInfo.max >= x.value) { isBST = false ; } if (rightInfo != null && rightInfo.min <= x.value) { isBST = false ; } return new Info(isBST, max, min); }
完全二叉树
如何判断一个二叉树是完全二叉树
完全二叉树:一颗二叉树从左到右是依次变满的,即使不满,也是变满的样子
解题:二叉树宽度遍历,1.任何一个节点如果有有节点,没左节点,false;2.在第一个条件不违规情况,如果遇到第一个左右两个节点不双全情况,接下来遇到的所有节点,必须是叶子节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public static boolean isCBT (Node head) if (head == null ) { return true ; } LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); boolean leaf = false ; Node l = null ; Node r = null ; queue.add(head); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { head = queue.poll(); l = head.left; r = head.right; if ((leaf && (l != null || r != null )) || (l == null && r != null )) { return false ; } if (l != null ) { queue.add(l); } if (r != null ) { queue.add(r); } if (l == null || r == null ) { leaf = true ; } } return true ; }
平衡二叉树
如何判断一棵树是平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树特性: 对于任何一个子树来说,左树的高度和右树的高度差,都不超过1解决思路: 假设我可以向我的左树要信息,可以向右树要信息,如果我整棵树是平衡二叉树,我左树得是平的,右树得是平的,对于X节点来说,左树-右树高度差<=1;我向左树要信息:1.是否是平的;2.高度是多少,右树要信息:1.是否是平的;2.高度是多少
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static class Info public boolean isBalanced; public int height; public Info (boolean i, int h) isBalanced = i; height = h; } } public static Info process (Node x) if (x == null ) { return new Info(true , 0 ); } Info leftInfo = process(x.left); Info rightInfo = process(x.right); int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1 ; boolean isBalanced = true ; if (!leftInfo.isBalanced) { isBalanced = false ; } if (!rightInfo.isBalanced) { isBalanced = false ; } if (Math.abs(leftInfo.height - rightInfo.height) > 1 ) { isBalanced = false ; } return new Info(isBalanced, height); }
满二叉树
如何判断一棵树是满二叉树
树最大深度L,节点个数N,满足N=2(L次方)-1
解法(递归套路): 先求二叉树最大深度L,再求节点个数N,满足N=2(L次方)-1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public static class Info public int height; public int nodes; public Info (int h, int n) height = h; nodes = n; } } public static boolean isFull (Node head) if (head == null ) { return true ; } Info all = process(head); return (1 << all.height) - 1 == all.nodes; } public static Info process (Node head) if (head == null ) { return new Info(0 , 0 ); } Info leftInfo = process(head.left); Info rightInfo = process(head.right); int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1 ; int nodes = leftInfo.nodes + rightInfo.nodes + 1 ; return new Info(height, nodes); }
二叉树最低公共祖先
给定两个二叉树节点node1和node2,找到他们的最低公共祖先节点
解法1:遍历整棵树,把所有节点的父节点都维护到一个Map中,然后找到node1的所有父节点维护到set中,再遍历node2的所有的父,第一个在set中遇到的节点就是最低公共祖先
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public static Node lca (Node head, Node o1, Node o2) if (head == null ) { return null ; } HashMap<Node, Node> parentMap = new HashMap<>(); parentMap.put(head, null ); fillParentMap(head, parentMap); HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>(); Node cur = o1; set.add(cur); while (null != parentMap.get(cur)) { cur = parentMap.get(cur); set.add(cur); } cur = o2; while (!set.contains(cur)) { cur = parentMap.get(cur); } return cur; } private static void fillParentMap (Node head, HashMap<Node, Node> fatherMap) if (head.left != null ) { fatherMap.put(head.left, head); fillParentMap(head.left, fatherMap); } if (head.right != null ) { fatherMap.put(head.right, head); fillParentMap(head.right, fatherMap); } }
解法2(非常抽象):可能的情况有1:node1和node2互为公共祖先;2:node1和node2不互为公共祖先;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static Node lowestCommonAncestor (Node head, Node o1, Node o2) if (head == null || head == o1 || head == o2) { return head; } Node left = lowestCommonAncestor(head.left, o1, o2); Node right = lowestCommonAncestor(head.right, o1, o2); if (left != null && right != null ) { return head; } return left != null ? left : right; }
图
常见的表示图的方法:临接表法,和临接矩阵法,数组等
做模板,然后把所有的图的问题转化为自己熟悉的数据结构,带着模板上考场
图的宽度优先遍历 约瑟夫圆环问题 逆波兰计算器
实现一个计算器,只有加减乘除法,没有括号,输入是一个字符串如10+2+3*5
解题:表达式转化为后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 public static void main (String[] args) String str = "10+2+3*5" ; String[] strArr = changeStrArr(str); List<String> polandList = polandNotation(strArr); System.out.println(polandList); System.out.println(calculate(polandList)); } private static String[] changeStrArr(String str) { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (char c : str.toCharArray()) { if ("+-*/" .contains(String.valueOf(c))) { stringBuilder.append(";" ); stringBuilder.append(c); stringBuilder.append(";" ); } else { stringBuilder.append(c); } } return stringBuilder.toString().split(";" ); } private static List<String> polandNotation (String[] str) List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>(); Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>(); for (String itm : str) { if (itm.matches("\\d+" )) { s2.add(itm); } else { while (!s1.isEmpty() && Operation.getValue(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(itm)) { s2.add(s1.pop()); } s1.push(itm); } } while (!s1.isEmpty()) { s2.add(s1.pop()); } return s2; } private static class Operation private static int ADD = 1 ; private static int SUB = 1 ; private static int MUL = 2 ; private static int DIV = 2 ; public static int getValue (String operation) int result = 0 ; switch (operation) { case "+" : result = ADD; break ; case "-" : result = SUB; break ; case "*" : result = MUL; break ; case "/" : result = DIV; break ; default : break ; } return result; } } private static int calculate (List<String> polandList) Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); for (String itm : polandList) { if (itm.matches("\\d+" )) { stack.push(itm); } else { int num2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); int num1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); int res = 0 ; if (itm.equals("+" )) { res = num1 + num2; } else if (itm.equals("-" )) { res = num1 - num2; } else if (itm.equals("*" )) { res = num1 * num2; } else if (itm.equals("/" )) { res = num1 / num2; } else { throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误" ); } stack.push(String.valueOf(res)); } } return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop()); }
前缀树 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 public static class Node1 public int pass; public int end; public Node1[] nexts; public Node1 () pass = 0 ; end = 0 ; nexts = new Node1[26 ]; } } public void insert (String word) if (word == null ) { return ; } char [] str = word.toCharArray(); Node1 node = root; node.pass++; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++) { path = str[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[path] == null ) { node.nexts[path] = new Node1(); } node = node.nexts[path]; node.pass++; } node.end++; } public int search (String word) if (word == null ) { return 0 ; } char [] chs = word.toCharArray(); Node1 node = root; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { index = chs[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[index] == null ) { return 0 ; } node = node.nexts[index]; } return node.end; } public int prefixNumber (String pre) if (pre == null ) { return 0 ; } char [] chs = pre.toCharArray(); Node1 node = root; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { index = chs[i] - 'a' ; if (node.nexts[index] == null ) { return 0 ; } node = node.nexts[index]; } return node.pass; } public void delete (String word) if (search(word) != 0 ) { char [] chs = word.toCharArray(); Node1 node = root; node.pass--; int path = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < chs.length; i++) { path = chs[i] - 'a' ; if (--node.nexts[path].pass == 0 ) { node.nexts[path] = null ; return ; } node = node.nexts[path]; } node.end--; } }
贪心算法 在某一个标准下,优先考虑最满足标准的样本,最后考虑最不满足标准的样本,最终得到一个答案的算法,叫做贪心算法。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,所做出的是某种意义上的局部最优解。
会议室占用问题 问题:只有一个会议室,多个会议占用会议室的时间有冲突,如何让会议室进行的会议最多,返回最多的会议场次
解:哪个会议结束时间早,就优先安排,然后接下来继续找下一个会议结束时间早的会议
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public static class Program public int start; public int end; public Program (int start, int end) this .start = start; this .end = end; } } public static class ProgramComparator implements Comparator <Program > @Override public int compare (Program o1, Program o2) return o1.end - o2.end; } } public static int bestArrange2 (Program[] programs) Arrays.sort(programs, new ProgramComparator()); int timeLine = 0 ; int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < programs.length; i++) { if (timeLine <= programs[i].start) { result++; timeLine = programs[i].end; } } return result; }
八皇后问题 多线程相关 三个线程交替打印
三个线程交替打印,1线程打印1;2线程打印2;3线程打印3;1线程打印4……一直打印到100
解题方式由很多,无非就是涉及到线程通信问题以及修改共享变量问题
题解1: 不加锁,利用线程可见性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class ThreadPrint private static volatile int i = 0 ; private static volatile int flag = 0 ; public static void main (String[] args) Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Thread1()); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Thread2()); Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Thread3()); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); } public static class Thread1 implements Runnable public void run () while (i <= 100 ) { if (flag == 0 ) { System.out.println("t1=" + i); i++; flag = 1 ; } } } } public static class Thread2 implements Runnable public void run () while (i <= 100 ) { if (flag == 1 ) { System.out.println("t2=" + i); i++; flag = 2 ; } } } } public static class Thread3 implements Runnable public void run () while (i <= 100 ) { if (flag == 2 ) { System.out.println("t3=" + i); i++; flag = 0 ; } } } } }
题解2 :LockSupport 实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 public class ThreadPrint2 private static int number = 1 ; private static Thread thread1, thread2,thread3; public static void main (String[] args) thread1 = new Thread(ThreadPrint2::thread1, "thread1" ); thread2 = new Thread(ThreadPrint2::thread2, "thread2" ); thread3 = new Thread(ThreadPrint2::thread3, "thread3" ); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); } public static void thread1 () while (ThreadPrint2.number <= 100 ) { System.out.println("thread1:" + ThreadPrint2.number); ThreadPrint2.number++; LockSupport.unpark(thread2); LockSupport.park(); } } public static void thread2 () while (ThreadPrint2.number <= 100 ) { LockSupport.park(); System.out.println("thread2:" + ThreadPrint2.number); ThreadPrint2.number++; LockSupport.unpark(thread3); } } public static void thread3 () while (ThreadPrint2.number <= 100 ) { LockSupport.park(); System.out.println("thread3:" + ThreadPrint2.number); ThreadPrint2.number++; LockSupport.unpark(thread1); } } }
题解3 :经典实现 实现wait->notifyAll
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 public class ThreadPrint3 private static int count = 1 ; public static void main (String[] args) Object lock = new Object(); new Thread(() -> { try { synchronized (lock) { while (count <= 100 ) { if (count % 3 == 1 ) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + count); count++; } lock.notifyAll(); lock.wait(); } lock.notifyAll(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "T1" ).start(); new Thread(() -> { try { synchronized (lock) { while (count <= 100 ) { if (count % 3 == 2 ) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + count); count++; } lock.notifyAll(); lock.wait(); } lock.notifyAll(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "T2" ).start(); new Thread(() -> { try { synchronized (lock) { while (count <= 100 ) { if (count % 3 == 0 ) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + count); count++; } lock.notifyAll(); lock.wait(); } lock.notifyAll(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }, "T3" ).start(); } }
题解4 :Lock实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class ThreadPrint4 private static int cnt = 0 ; public static void main (String[] args) Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition c1 = lock.newCondition(); Condition c2 = lock.newCondition(); Condition c3 = lock.newCondition(); new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { while (cnt <= 100 && cnt % 3 == 0 ) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---->" + cnt); cnt++; c2.signal(); c1.await(); } c3.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "T1" ).start(); new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { while (cnt <= 100 && cnt % 3 == 1 ) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---->" + cnt); cnt++; c3.signal(); c2.await(); } c1.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "T2" ).start(); new Thread(() -> { lock.lock(); try { while (cnt <= 100 && cnt % 3 == 2 ) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---->" + cnt); cnt++; c1.signal(); c3.await(); } c2.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } }, "T3" ).start(); } }
其他算法题